Exercise 13.3
Question 1
(i) If $^n{\mathrm{P}_{4}}=12 \times ^{n} \mathrm{P}_{2}$ , find nSol :
$^{n} P_{4}=12 \times \!^nP_2$
$\dfrac{^n{P_{4}}}{^n{P_{2}}}=12$
[$^n P_r=\frac{n!}{(n-r)!}$]
$\frac{\frac{n !}{(n-4) !}}{\frac{n !}{(n-2) !}}=12$
$\frac{(n-2) !}{(n-4) !}=12$
$\frac{(n-2)(n-3)(n-4) !}{(n-4) !}=12$
(n-2)(n-3)=4×3
$\begin{array}{r|l} n-2=4 & n-3=3 \\n=4+2=6 &n=3+3=6\end{array}$
(ii) If $^{n} \mathrm{P}_{5}=20 \times^{n} \mathrm{P}_{3}$ find the value of n
Sol :
$^n{P}_5=20 \times \!^{n} P_{3}$
$\frac{^n P_{5}}{^n P_{3}}=20$
[$^n P_r=\frac{n!}{(n-r)!}$]
$\frac{\frac{n!}{(n-5) !}}{\frac{n !}{(n-3) !}}=20$
$\frac{(n-3) !}{(n-5) !}=2$
$\frac{(n-3)(n-4)(n-5) !}{(n-3)!}=20$
(n-3)(n-4)=20
(n-3)(n-4)=5×4
$\begin{array}{r|l} n-3=5 & n-4=4 \\ n=5+3 & n=4+4 \\ n=8 & n=8\end{array}$
Question 2
(i) If $^n{\mathrm{P}_{4}}: \!^n+\!^1 \mathrm{P}_{4}=3: 4$ , find nSol :
$^{n}P_{4}:\!^{n+1} P_{4}=3: 4$
$\frac{^n{P_{4}}}{^{n+1}{P_{4}}}=\frac{3}{4}$
[$^n P_r=\frac{n!}{(n-r)!}$]
$\frac{\frac{n !}{(n-4) !}}{\frac{(n+1) !}{(n+1-4)!}}=\frac{3}{4}$
$\frac{n!}{(n-4) !} \times \frac{(n-3) !}{(n+1) !}=\frac{3}{4}$
$\frac{n !}{(n-4) !} \times \frac{(n-3)(n-4) !}{(n+1) n !}=\frac{3}{4}$
$\frac{n-3}{n+1}=\frac{3}{4}$
4n-12=3n+3
4n-3n=3+12
n=15
(ii) If $\frac{^n{\mathrm{P}_{4}}}{^{n-1} \mathrm{P}_{4}}=\frac{5}{3}, n>4$ find n
Sol :
[$^n P_r=\frac{n!}{(n-r)!}$]
$\frac{\frac{n !}{(n-4) !}}{\frac{(n-1) !}{(n-1-4) !}}=\frac{5}{3}$
$\frac{n !}{(n-4) !} \times \frac{(n-5) !}{(n-1) !}=\frac{5}{3}$
$\frac{n(n-1) !}{(n-4)(n-5) !} \times \frac{(n-5) !}{(n-1) !}=\frac{5}{3}$
$\frac{n}{n-4}=\frac{5}{3}$
3n=5n-20
3n-5n=-20
-2n=-20
$n=\frac{20}{2}=10$
Question 3
r ज्ञात कीजिए यदि
[Find r if]
Sol :
$\frac{5 !}{(5-r) !}=\frac{6 !}{(6-r+1) !}$
$\frac{5 !}{(5-r) !}=\frac{6 !}{(7-r) !}$
$\frac{(7-r) !}{(5-r) !}=\frac{6 !}{5 !}$
$\frac{(7-r)(6-r)(5-r) !}{(5-r) !}=\frac{6 \times 5 !}{5 !}$
(7-r)(6-r)=6
(7-r)(6-r)=3×2
$\begin{array}{r|l}7-r=3&6-r=2\\7-3=r&6-2=r\\4=r&4=r\end{array}$
(ii) $^{5} P_{r}=2.^{6} P_{r-1}$
Sol :
$\frac{5 !}{(5-r) !}=2 \cdot \frac{6 !}{(6-r+1) !}$
$\frac{5 !}{(5-r) !}=2 \cdot \frac{6 !}{(7-r) !}$
$\frac{(7-r) !}{(5-r) !}=2 \cdot \frac{6 !}{5 !}$
$\frac{(7-r)(6-r)(5-r) !}{(5-r) !}=\frac{2 \times 6 \times 5 !}{5 !}$
(7-r)(6-r)=12
(7-r)(6-r)=4×3
$\begin{array}{r|l}7-r=4&6-r=3\\7-4=r&6-3=r\\3=r&3=r\end{array}$
Question 4
यदि (If) ${ }^{20} \mathrm{P}_{r}=6840, r$ ज्ञात कीजिए (find r)।So :
Question 5
यदि (If) $^{k+5} P_{k+1}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}.^{k+3} P_{k}$ , ज्ञात कीजिए (find k)
Sol :
$\frac{^{k+5} P_{k+1}}{^{k+3} P_{k}}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{\frac{(k+5) !}{(k+5-k-1) !}}{\frac{(k+3) !}{(k+3-k) !}}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{\frac{(k+5) !}{4 !}}{\frac{(k+3) !}{3 !}}=\frac{1 1(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{(k+5) !}{4 !} \times \frac{3 !}{(k+3) !}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{(k+5)(k+4)(k+3) !}{4 \times 3 !} \times \frac{3 !}{(k+3) !}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{(k+5)(k+4)}{4}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$(k+5)(k+4)=\frac{11(k-1)}{2} \times 4$
$k^{2}+4 k+5 k+20=22(k-1)$
$k^{2}+9 k+20=22 k-22$
$k^{2}+9 k+20-22 k+22=0$
$k^{2}-13 k+42=0$
$k^{2}-6 k-7 k+42=0$
k(k-6)-7(k-6)=0
(k-6)(k-7)=0
$\begin{array}{r|l}k-6=0 &k-7=0 \\ k=6& k=7\end{array}$
Sol :
$\frac{^{k+5} P_{k+1}}{^{k+3} P_{k}}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{\frac{(k+5) !}{(k+5-k-1) !}}{\frac{(k+3) !}{(k+3-k) !}}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{\frac{(k+5) !}{4 !}}{\frac{(k+3) !}{3 !}}=\frac{1 1(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{(k+5) !}{4 !} \times \frac{3 !}{(k+3) !}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{(k+5)(k+4)(k+3) !}{4 \times 3 !} \times \frac{3 !}{(k+3) !}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$\frac{(k+5)(k+4)}{4}=\frac{11(k-1)}{2}$
$(k+5)(k+4)=\frac{11(k-1)}{2} \times 4$
$k^{2}+4 k+5 k+20=22(k-1)$
$k^{2}+9 k+20=22 k-22$
$k^{2}+9 k+20-22 k+22=0$
$k^{2}-13 k+42=0$
$k^{2}-6 k-7 k+42=0$
k(k-6)-7(k-6)=0
(k-6)(k-7)=0
$\begin{array}{r|l}k-6=0 &k-7=0 \\ k=6& k=7\end{array}$
Question 6
यदि (If) ${ }^{22} P_{r+1}:{ }^{20} \mathrm{P}_{r+2}=11: 52, r$ ज्ञात कीजिए (find r.)।Sol :
Question 7
If $^{m+n}{\mathrm{P}_{2}}=90$ and $^{m-n} \mathrm{P}_{2}=30$ , m और n ज्ञात कीजिए ( find m and n.)Sol :
$^{m+n}P_{2}=90$
$\frac{(m+n) !}{(m+n-2) !}=90$
$\frac{(m+n)(m+n-1)(m+n-2) !}{(m+n-2) !}=90$
(m+n)(m+n-1)=90
(m+n)(m+n-1)=10×9
$\begin{array}{r|l}m+n=10& m+n-1=9 \\& m+n =10..(i) \end{array}$
Now ,
$^{m-n}P_{2}=30$
$\frac{(m-n) !}{(m-n-2) !}=30$
$\frac{(m-n)(m-n-1)(m-n-2) !}{(m-n-2) !}=30$
(m-n)(m-n-1)=30
(m-n)(m-n-1)=6×5
$\begin{array}{r|l}m-n=6 &m-n-1=5 \\ &m-n=6..(i)\end{array}$
From equation (i) and (ii)
$\begin{aligned} m+n &=10 \\ m-n &=6 \\ \hline2 m &=16 \end{aligned}$
$m=\frac{16}{2}=8$
[]
m+n=10
8+n=10
n=10-8=2
∴ m=8 , n=2
Question 8
यदि (If) $^{12} \mathrm{P}_{r}=11880$ r ज्ञात कीजिए ( Find r )Sol :
$\frac{12 !}{(12-r) !}=11880$
$\frac{479001600}{(12-r)!}=11880$
$\frac{479001600}{11880}=(12-r)!$
40320=(12-r)!
8!=(12-r)!
8=12-r
r =4
Question 9
यदि (If) ${ }^{56} \mathrm{P}_{r+6}:{ }^{54} \mathrm{P}_{r+3}=308000: 1, r$ ज्ञात कीजिए (find r.)Sol :
Question 10
1 से 9 तक के अंको को प्रयोग करके कितने 3 अंकीय संख्याएँ बन सकती है, यदि किसी भी अंक को दोहराया नही गया है?[How many 3-digit numbers can be formed by using the digits 1 to 9 if no digit is repeated?]
Sol :
9 अंको मे 3 अंको को एक साथ लेकर बने 3 अंकीय संख्या को लिखने का तरिका= 9P3
$=\frac{9!}{(9-3)!}$
$=\frac{9 !}{6 !}$
$=\frac{9\times 8\times 7\times 6!}{6!}$
=504
1 से 9 तक के अंक
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9
Question 11
1 से 9 तक के अंकों का प्रयोग करके कितनी 4 अंकीय संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं , यदि अंको की पुनरावृति की अनुमति नहीं है?
[How many 4-digit numbers can be formed by using the digits 1 to 9 if repetition of digits is not allowed]
Sol :
Question 12
किसी भी अंक को दोहराए बिना कितनी 4 अंकीय संख्याएँ होती हैं?
[How many 4-digit numbers are there with no digit repeated ?]
Sol :
Question 13
अंक 1,2,3,4,6,7 को प्रयुक्त करने से कितनी 3 अंकीय सम संखाएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं, यदि कोई भी अंक दोहराया नहीं गया है ?
[How many 3-digit even numbers can be made using the digits 1,2,3,4,5,6,7, if no digit is repeated?]
Sol :
Question 14
अंक 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 के उपयोग द्वारा कितनी 4 अंकीय संख्याएँ बंनाई जा सकती हैं, यदि कोई भी अंक दोहराया नहीं गया है ? इनमें से कितनी सम संख्याएँ होंगी ?
[Find the number of 4-digit numbers that can be formed using the digits 1,2,3,4,5, if no digit is repeated. How many of these will be even]
Sol :
Question 15
0,1,3,5,7 तथा 9 अंकों से, 10 से विभाजित होने वाली और बिना पुनरावृत्ति किए कितनी 6 अंकीय संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ?
[How many 6-digit number can be formed from the digits 0,1,3,5,7, and 9 which are divisible by 10 and no digit is repeated ?]
Sol :
Question 16
अंक 1,2,4,5,7 से चार अंकों की कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं? कोई अंक एक ही संख्या में दुबारा न आए।[How many numbers of four digits can be formed with the digits 1,24,5,7 no digit being repeated?]
Sol :
Sol :
Question 17
अंक 0,1,2,3,4, से 5 अंकों की कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं यदि अंकों की पुनरावृत्ति की अनुमती नहीं है।
[How many numbers of 5 digits can be formed with the digits 0,1,2,3,4?]
Sol :
Question 18
1,2,3,4,5,6,7 अंकों से 100 और 1000 के बीच कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ? किसी अंक का पुनरावृत्ति नहीं होता है।
[How many numbers between 100 and 1000 can be formed with the digits 1,2,3,4,5,6,7; no digits being repeated?]
Sol :
Question 19
2. 3,4,5,6,0 अंकों से 300 और 1000 के बीच किसी अंक का पुनरावृत किये बिना कितनी संख्याएँ बन सकती हैं ?
[How many numbers between 3.00 and 1000 can be made with the digits 2,3,4,5,6,0]
Sol :
Question 20
2,3,4,0,8,9 अंकों से 100 और 1000 के बीच किसी अंक का पुनरावृत किये बिना कितनी संख्याएँ बन सकती है?
[How many numbers each lying between 100 and 1000 can be formed with digits 2,3,4,0,8,9 ; no digit being repeated?]
Sol :
Question 21
100 से 1000 के बीच स्थित कितनी संख्याएँ हैं, जिन्हें अंक 0,1,2,3,4,5 से बनाया जा सकता है, यदि अंकों के पुनरावृत्ति की अनुमति नहीं है।
[How many numbers lying between 100 and 1000 can be formed with the digits 0,1,2,3,4,5 if the repetition of the digits is not allowed]
Sol :
Question 22
9 अंकों की वैसी सभी संख्याओं की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए जिसमें सभी भिन्न अंक हों
[Find the total numbers of nine digit numbers which have all different digits.]
Sol :
Question 23
0,1,2,3,4,5 अंको से 1000 और 10000 के बीच कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती है? कोई अंक एक ही संख्या में दुबारा न आए।
[How many numbers each lying between 1000 and 10000 can be formed with the digits 0,1,2,3,4,5; no digit being repeated ?
Sol :
Question 24
0,1,5,9 अंकों से 5000 से अधिक कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ? किसी अंक का पुनरावृत्त नहीं होता है।
[How many different numbers greater than 5000 can be formed with the digits $0,1,5,9 ;$ no digit being repeated ?]
Sol :
Question 25
यदि अंकों की पुनरावृत्ति नहीं हो तो 0,4,5,6,7 अंकों से 5 से विभाजित होने वाली कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ?
[If repetition of digits is not allowed how many numbers of four digits divisible by 5 can be formed with digits 0,4,5,6,7?]
Sol :
Question 26
अंक 4,5,6,7,8,9 से 6 अंकों की कितनी विभिन्न संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं? उनमें से कितनी संख्याएँ 5 से विभाज्य हैं ? एक ही संख्या में कोई अंक दुबारा नहीं आता है।
[How many different numbers of 6 digits each can be formed with the digits 4,5,6,7,8,9 ? How many of them are not divisible by 5 ; no digit being repeated.]
Sol :
Question 27
अंक 1,2,3,4 और 5 से 5 अंकों की कितनी सम संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ?
[How many even numbers of 5 digits can be formed with the digits 1 ,2,3,4 and 5]
Sol :
Question 28
1000 से छोटी 5 से विभाज्य कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं जिसमें किसी संख्या में कोई भी अंक एक से अधिक बार नहीं आता है ?
[How many numbers less than 1000 and divisible by 5 can be formed in which no digit occurs more than once in the same number]
Sol :
Question 29
ज्ञात कीजिए कि अंक 0,4,5,6,7,8 से 100 और 999 के बीच कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं, किसी भी अंक का एक बार से अधिक प्रयोग नहीं होता है। उनमें कितनी विषम संख्याएँ हैं ?
[Find how many numbers between 100 and 999 can be formed with the digits 0,4,5,6,7,8; no digit being used more than once. How many of them are odd?]
Sol :
Question 30
0,1,2,3,4,5 से कितनी विषम संख्याएँ बन सकती हैं, यदि किसी भी संख्या में कोई भी अंक दुबारा नहीं आएगा ?
[How many odd numbers can be formed using 0,1,2,3,4,5 if the digits are not repeated in the same number?]
Sol :
Question 31
1,2,3,4,5, 6 अंकों से 6 अंकों की बनने वाली संख्याओं की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए जिनके दहाई स्यान का अंक 5 हो।
[Find the number of numbers of six digits formed with the digits 1,2,3,4,5,6 in which 5 always occurs in the tens place.]
Sol :
Question 32
अंक 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 से 4 अंकों की संख्या बनाई जाती है। ज्ञात कीजिए
(i) इस तरह की कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ?
(ii) उनमें कितनी संख्याएँ 3400 से बड़ी हैं?
[A number of four different digits is formed by using the digits 1,2,3,4,5,6,7
(i) How many such numbers can be formed ?
(ii) How many of them are greater than 3400]
Sol :
Question 33
1,2,3,4,5 अंकों से 4 अंकों की बनने वाली -उन संख्याओं की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए जिनके इकाई स्थान का अंक 5 तथा हजार स्थान का अंक 3 है।
[Find the number of numbers of 4 digits formed with the digits 1,2,3,4,5 in which 3 occurs in the thousands place and 5 occurs in the units place]
Sol :Question 34
0,1,2,3,4,5 अंकों में-से किसी अंक का प्रयोग कर कितने धन पूर्णाक बनाये जा सकते हैं; प्रत्येक संख्या में किसी भी अंक का प्रयोग एक से अधिक बार नहीं हों। इन पूर्णाकों में कितने 3000 से बड़े हैं ?
[Find the number of positive integers which can be formed by using any number of digits from 0,1,2,3,4,5 but using each digit not more than once in each number. How many of these integers are greater than 3000?]
Question 35
अंक 0,1,2,3,5,7,9 में से किसी अंक का प्रयोग कर कितनी संख्याएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं ?
[How many numbers can be formed by using any number of the digits 0,1,2,3,5,7,9 ?]
Sol :
Question 36
एक नौकर को 5 पत्र डाक में छोड़ने हैं। यदि वहाँ 4 पत्र-मंजूषा हों - तो वह कितने प्रकार से पत्र छोड़ सकता है ?
[A servant has to post 5 letters and there are 4 letter boxes. In how many ways can he post the letters?]
Sol :
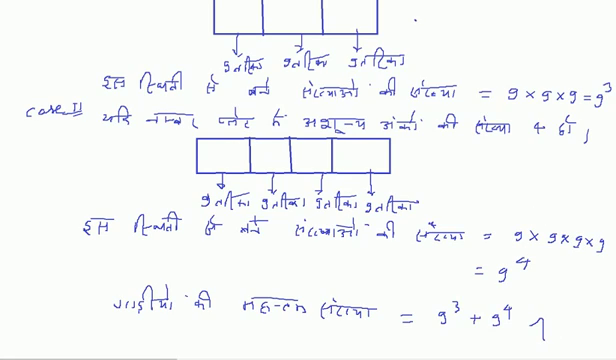
n असमान वस्तुओं में से r वस्तुएँ छेकर बनाये गये क्रमचंयों की संख्या निकालना जबकि प्रत्येक वस्तु क्रमचय में r बार तक आ सकती है = $n^{r}$
Question 37
तीन इनामों को 5 विद्यार्थियों को कितने तरीकों से दिया जा सकता है जबकि प्रत्येक विद्यार्थी कोई भी इनाम पाने के योग्य है ?
[In how many ways can three prizes be given away to 5 students when each student is eligible for any of the prizes ?]
Sol :
Question 38
कितने तरीकों से n चीजों को p व्यक्तियों को दिया जा सकता है, जबकि प्रत्येक व्यक्ति कुछ भी संख्या में चीज पा सकता है ?
[In how many ways can $n$ things be given to p persons, when each person can get any number of things (n>p) .]
Sol :
Question 39
निम्नांकित 5 इनामों को कितने विभिन्न तरीकों से 10 विद्यार्थियों में वितरित किया जा सकता है ? प्रथम और द्वितीय गणित में, प्रथम और द्वितीय भौतिकी में तथा प्रथम हिन्दी में।
[In how many different ways the following 5 prizes be distributed among 10 students? First and second in Mathematics; find and second in physics and first in Hindi]
Sol :
Question 40
5 प्रदिनिधियों को किसी शहर के 6 होटलों में कितने तरीकों से ठहराया जा सकता है, यदि किसी तरह का प्रतिबंध न हो?
[In how many ways 5 delegates can be put in 6 hotels of a city if there is no restriction ?]
Sol :
Question 41
अंक 0. 1. 2. 3 और 4 से 5 अंकों की संख्याओं की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए यदि अंकों की पुनरावृत्ति होती है।
[Find the number of numbers of 5 digits that can be formed with the digits 0,1,2,3,4 if repetition of digits is allowed]
Sol :
Question 42
चार अँगुलियों में 6 भिन्न अगूंठियों को कितना तरीकों से पहना जा सकता है ?
[In how many ways 6 rings of different type can be had in 4 fingers ?]
Sol :
Question 43
अंक 0,1,2,3,4 और 5 से 4 अंकों की 3000 से बड़ी संख्याओं की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए, यदि अंकों की पूनरावृत्ति होती है।
[Find the number of numbers of 4 digits greater than 3000 that can be formed with the digits 0,1,2,3,4 and 5 if repetition of digits is allowed]
Sol :
Question 44
किसी शहर में गाड़ियों के नम्बर प्लेट में अशून्य अंको की संख्या 3 या 4 है ।
गाड़ियों की महत्तम संख्या क्या है जिन्हें अंकित किया जा सकता है?
[In a town the car plate numbers contains only three or four digits, not containing the digit 0. What is the maximum number of cars that can be numbered?]
Sol :
Question 45
बहुविकल्पीय परीक्षा के 10 प्रश्नों का उत्तर कितने तरीकों से दिया जा सकता है, के प्रत्येक प्रश्न के लिए a, b, c, d चार विकल्प दिये गये हों ? यदि दो लगातार प्रश्नों के उत्तर नहीं करना हों तो कितने तरीके हो सकते हैं?
[In how many ways can a ten question multiple choice examination be answered if there are four choices, a, b, c and d to each question ? If no two consecutive questions are answered the same, how many ways are there ?]
Sol :





























































Wow fantastic
ReplyDeleteThis app is Right